Many Ethereum layer-2 scaling solutions have emerged over the years, each aiming to make the leading smart contract-enabled blockchain more efficient. This guide zeroes in on Mantle Network, a solution that’s taking Ethereum scaling to a whole new level. Read on to find out what Mantle is, how it works, and why it’s different from other Ethereum L2s.
What is Mantle Network?
Mantle Network is an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible Layer-2 (L2) scaling solution. It uses Optimistic rollups to facilitate cheap and fast transactions. The network achieves this by bundling and executing transactions off-chain, but all transactions ultimately settle on-chain. Mantle’s founders are anonymous.
In May 2023, Mantle merged with the BitDAO ecosystem, creating a unified ecosystem under one brand and token: Mantle (MNT). The co-founders of the centralized exchange Bybit, Daniel Yan and Ben Zhou, established BitDAO in June 2021. The decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is well-known for its substantial treasury.
After merging with BitDAO in May, Mantle unveiled mainnet alpha in July 2023 at the EthCC in Paris.
Before the launch, Mantle underwent a six-month testnet phase where it processed more than 14 million on-chain transactions.
How does Mantle work?
Modular design
Mantle takes scaling a notch higher with its modular design that combines Optimistic rollups with a separate data availability layer. So, instead of performing the four key blockchain functions on a single network layer as most monolithic blockchains do, Mantle handles these processes on different layers.
The transaction execution function takes place on Mantle’s EVM-compatible execution settlement layer. Mantle’s sequencer generates blocks on the L2 execution layer and submits state root data to the main blockchain.
The Ethereum L1 network takes care of the consensus and settlement functions.
Mantle performs the final function, data availability, with the help of EigenDA technology. Eigen Data Availability (EigenDA) stores callback data that would typically be broadcast to L1 in conventional rollups. EigenDA is a data availability layer built on the EigenLayer.
The diagram below illustrates an example of modular chain design.
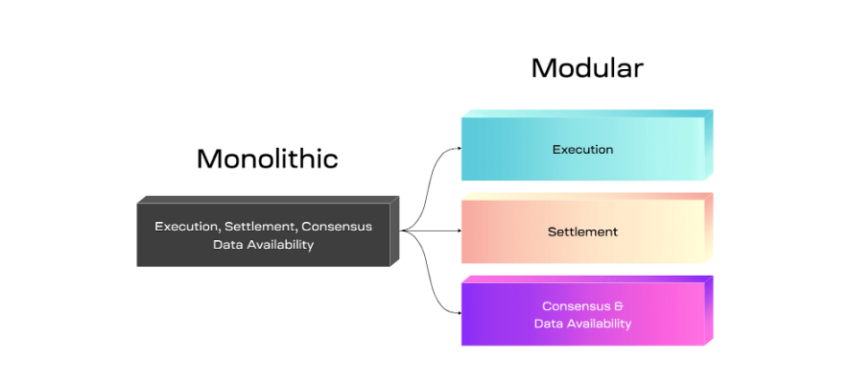
Mantle’s modular architecture significantly lowers transaction costs compared to the base layer. It also improves network efficiency thanks to the separated layers while minimizing the overall load on nodes with Optimistic rollups.
What is the EigenLayer?
The EigenLayer is a decentralized Ethereum protocol that enables ETH restaking. It allows the EigenDA-powered Mantle data availability layer to derive security from Ethereum. This means Ethereum stakers can restake ETH using pegged digital assets like rETH and stETH to secure Mantle’s data availability layer.
Besides helping make the Mantle data availability layer highly secure, the EigenLayer also offers high transaction throughputs that could reach 1 TB per second or more.
Network participants
Mantle Network has four nodes: sequencers, rollup verifiers, DA nodes, and Threshold Signature Scheme nodes (TSS).
Sequencers receive users’ transactions in real-time, generate blocks on L2, roll-up transactions into bundles with execution state roots, and publish block data to the base layer and L2. The initial Mantle sequencer is centralized. However, the project plans to decentralize it with time.
TSS nodes validate the transactions that the sequencers roll up into batches. After signing off these transactions, they broadcast the batches across Mantle.
/Related
More ArticlesRollup verifiers sync rollup data, initiate fraud proofs, and verify state roots from the sequencer. They also make block data available to users. Optimistic rollups assume batched transactions are valid unless someone challenges their credibility within the 7-day window. When this happens, the rollup initiates a fraud-proof to check for inaccuracies.
DA nodes store a copy of Mantle’s transaction data, making it easily accessible whenever necessary. These nodes also sign block data guaranteeing its usability when providing transaction data.
Transaction lifespan
The transactions lifespan on Mantle has the following three phases.
Initiation
During the initiation stage, a wallet user or DApp initiates a task. Performing this task costs money. Therefore, users must have enough money to settle the transaction fee. Also, they must sign the transaction with their private keys and submit it to Mantle. The sequencer node on the network then receives the transaction for processing.
Handling
The transaction activates a standard state verification process which the EVM software carries out. The verification process ensures that the transaction is valid and paid up. Next, the transaction updates the local state and becomes part of a pending block awaiting processing.
The sequencer then rolls up the transactions in the pending blocks into batches. These batches eventually settle on L1. Mantle spreads the fixed costs of the many transactions in a bundle to minimize user transaction fees.
Once the sequencer nodes have played their part, the TSS nodes come in to verify block data. The rollup verifiers also authenticate state roots at this stage.
Storage
The sequencer broadcasts the state root data across L2 and the main chain. Moreover, rollup verifiers sync the block data, making it available to users. On L1, the state root data goes through the consensus process, after which validators add it to the blockchain. DA nodes store the synced block data in exchange for MNT rewards.
Bridging
The Mantle bridge permits users to move digital assets from Ethereum to L2 and from L2 to Ethereum. Bridges are important since they enable interoperability between the connected networks while allowing the secure transfer of tokens to and from. A bridge is essentially a technology connecting L1 and L2 networks, L1 and L1 blockchains, or multiple L2 networks.
Governance
Mantle’s governance happens off-chain, where the core contributor team or community members can initiate discussions. The discussion initiator then introduces the topic on the forum where the broader community can view it. If the matter attracts enough positive interest, it progresses into a Mantle Improvement Proposal (MIP), which is similar to Ethereum EIPs.
Once MNT holders endorse the proposal, the core contributor team is responsible for implementing it. The core contributor team consists of growth and product development teams.
MNT holders can only vote once they delegate voting rights to themselves or a different eligible address. Delegation adjusts vote weight distribution among voters with divergent interests and areas of expertise.
“The key to Mantle’s success will be its ability to deliver on its technical promises while capitalizing on the growing demand for LSDFi solutions,”
DeFi Analyst Viktor DeFi: Medium
Functions of MNT & tokenomics
MNT is an ERC-20 token and the main asset used in the Mantle ecosystem after the merger. Based on this approved proposal, Mantle converted BIT tokens (the native BitDAO assets) to MNT. The conversion ratio was 1:1. However, the project did not convert the 3 billion BIT tokens in the treasury to MNT. Mantle will instead send the non-converted BIT tokens to a nominated burn address. BIT token holders received MNT tokens via an airdrop on July 17, 2023.
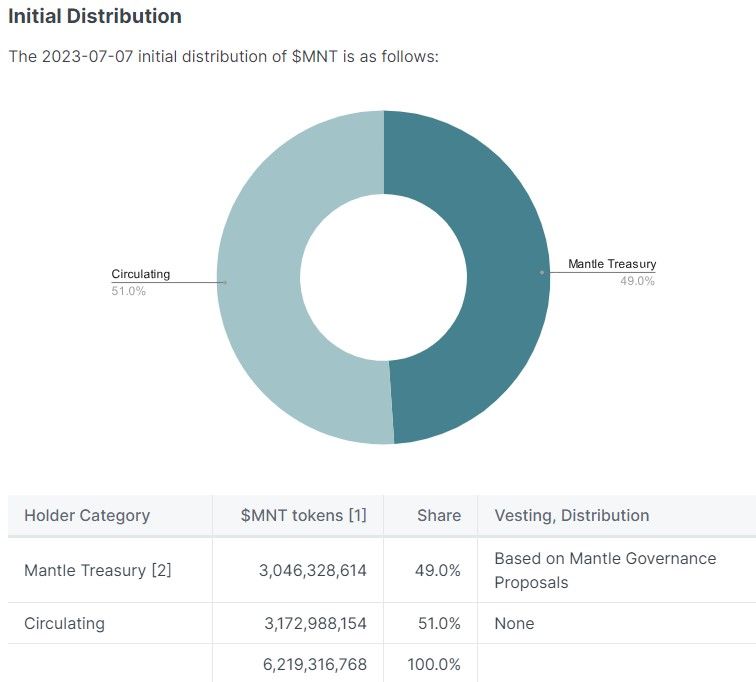
MNT is a utility and governance token. As a governance token, MNT gives holders the right to vote for or against ecosystem decisions. In that light, MNT holders passed a proposal that planned to cut down the MNT in the treasury from 6.05 billion to 3.05 billion. Also, the approved proposal maintained MNT’s circulating supply at 3.17 billion and decreased the fully diluted supply from 9.2 to 6.2 billion.
The proposal changed Mantle’s token distribution. Previously, the project allocated 65.6% MNT tokens to the treasury and 34.4% to the circulating supply. Now, the amount of tokens in the treasury and circulating supply stands at 49% and 51%, respectively.
As a utility token, Mantle users pay gas fees in MNT. Furthermore, Mantle Network nodes can use MNT as a collateral asset. This incentivizes nodes to participate in the network, keeping it stable and secure.
Mantle Network vs. other L2 networks
Mantle achieves hyperscaling while other L2 networks don’t
Generally, L2 networks find it difficult to hyper-scale because they rely on the monolithic architecture of base layers. As a result, the gas cost savings on these layers isn’t enough to support widespread adoption.
Mantle uses Optimistic rollups and a separate DA layer, allowing it to offer cheaper and faster transactions. This architecture differs from other Ethereum layer-2 scaling solutions like Cartesi, Loopring, Polygon, and Arbitrum. While Mantle isn’t the only L2 using a separate DA layer, its EigenDA-powered layer is decentralized. This differentiates it from other L2 networks using a centralized data availability layer.
Mantle’s security stems from Ethereum
Mantle leverages Ethereum’s consensus mechanism and validator set. This means Ethereum validators verify Mantle’s state transactions the same way they validate L1 transactions. Therefore, Mantle derives its security from the Ethereum blockchain, making it more secure than other L2 networks that utilize their own consensus models.
Potential use cases of Mantle
Gaming
Mantle’s modular design makes it ideal for gaming since it can support high transaction throughputs and low gas fees. This could encourage developers to build gaming DApps on Mantle where players can enjoy a near-frictionless experience. Mantle is working with Game7 and HyperPlay, projects that were BitDAO initiatives before the merger. The two projects focus on building vital tools for game developers.
Mantle has already started its journey of realizing this use case by adding the web3 gaming metaverse, Bullieverse, to its ecosystem. The metaverse project launched on Mantle in March 2023.
DeFi
Mantle can help advanced DeFi protocols built on it be affordable for widespread adoption. Increased DeFi adoption could encourage developers to create innovative financial products and services that are unavailable in the crypto space today.
Advantages of Mantle Network
Affordable transaction fees
Mantle Network slashes gas fees considerably. The project believes it can cut transaction costs by more than 80% thanks to batched transactions and its modular design. By bundling transactions into batches, gas fees are spread across the multiple transactions in each set.
It hyper-scales Ethereum
Mantle introduces a separate decentralized data availability layer with the help of EigenDA, allowing it to improve Ethereum’s efficiency. The EigenLayer can potentially achieve throughputs as high as 1TB/s or more. By leveraging the EigenDA, Mantle may offer its users higher transaction throughputs than the base layer.
It’s Ethereum-secured
Mantle transactions use the same validator sets and consensus process as Ethereum transactions. This means Ethereum validators add all Mantle transactions to Ethereum, allowing them to benefit from the security of one of the most secure blockchains in the industry.
Furthermore, Mantle’s DA layer derives its security from the Ethereum blockchain due to the EigenLayer. The protocol enables Ethereum stakers to restake their ETH using pegged assets like stETH, thereby securing the Mantle DA layer.
EVM Compatibility
Mantle Network is EVM-compatible, allowing developers to deploy Ethereum DApps on it. It also enables developers to use Ethereum smart contract development frameworks like Remix, Truffle, Hardhat, and Foundry on Mantle.
Disadvantages of Mantle Network
Mantle is still new
Mantle launched on the mainnet alpha in July 2023, so it has a long way to go before it can deliver its full potential. Moreover, the Mantle DAO is currently discussing critical proposals like ETH staking strategies and the possibility of leveraging a zkEVM.
Not fully decentralized, yet
The core Mantle team will initially use its own centralized sequencer node. Although it plans to make sequencer nodes decentralized in the future, it puts the network at risk of censorship resistance. Sequencers are in charge of receiving transactions and generating blocks. Putting this role in the hands of a centralized team puts users’ transactions at risk of censorship.
The Mantle Network doesn’t lack ambition
Mantle Network is an ambitious project striving to transform the L2 scaling landscape in new and innovative ways. It also shows that the industry is progressing nicely in its efforts to scale L1 blockchains and that the goal of elevated performance isn’t far from reach. So, it will be interesting to see how Mantle and other innovative L2 scaling solutions advance in the coming years.
Frequently asked questions
What is the Mantle network?
Is Mantle EVM compatible?
Why is it called Mantle?
Trusted
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.