With the rise of the crypto market, investors are looking for new cryptocurrencies to invest in while preserving their anonymity. The Uniswap decentralized exchange is an Automated Market Maker (AMM) that relies on smart contracts to swap tokens. So, what exactly is Uniswap, and how can you use it?
In this guide:
- How traditional crypto exchanges work
- Decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
- What is Uniswap?
- Liquidity pools on Uniswap
- Uniswap (UNI) token
- How do cryptocurrency swaps work?
- How to use Uniswap Exchange
- How to swap crypto on Uniswap Exchange
- How to add liquidity on Uniswap
- Uniswap vs. SushiSwap
- Should you use Uniswap?
- Frequently asked questions
How traditional crypto exchanges work

A crypto exchange is a trading platform that enables users to trade one cryptocurrency for other cryptos, cash, or other digital assets. There are two main types of cryptocurrency exchanges that exist today:
- Centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, etc.)
- Decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges (Uniswap, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, Curve, etc.)
In many aspects, the traditional crypto exchanges work similarly to regular stock exchanges, except that they are open 24/7.
Centralized crypto exchanges prevent anonymity with KYC
There are a few key differences between the two kinds of cryptocurrency exchanges. Firstly, the centralized crypto exchange requires users to complete the registration process before trading. This KYC (Know Your Customer) process is largely a legal requirement that combats money laundering.
The KYC process may require users to verify an email address, ID or passport photo, home address proof, phone verification, etc.
While most traditional crypto exchanges allow new users to create an account without an ID verification, they might limit features for that account. However, once the user’s identity is verified, many exchanges will allow users to link a bank account or a credit or debit card for fiat payments and withdrawals. These features usually come with special fees, just like bank accounts.

How centralized crypto exchanges generate revenue
Centralized crypto exchanges make money from offering crypto funding solutions for new crypto and blockchain projects, such as IEOs, STOs, and ICOs, and from their specific fees.
Traditional crypto exchanges charge a fee for:
- Trading (similar to the bank’s commission for bank accounts)
- Listing (Centralized crypto exchanges charge a fee for listing a new cryptocurrency)
- Deposit and withdrawal (these can be different for each exchange and for each particular cryptocurrency)
They also make use of order-book trading, where crypto traders can place buy or sell orders.
Market and limit orders on centralized exchanges
On a centralized exchange, such as Binance, the trader first places a buy or sell order. Then, the exchange sorts all orders by price, continually updating the list of orders as they take place.
There are two types main types of orders on centralized exchanges:
- Market orders: The exchange automatically buys/sells your funds for the best available price on the market.
- Limit orders: The traders place a buy/sell order at the desired price, and the exchange automatically executes it when the offer meets the price of the order.
The amount of open buy and sell limit orders represent the market depth.
How do market and limit orders work?
Exchanges always have a lot of sell orders listed. For instance, if you want to buy bitcoin, you can either place a market order, which will automatically get the funds at the best available price, or place a limit order.
When placing a limit order, you can indicate the desired place at which the order execution must take place. Limit orders support partial fulfillment, put on hold until a new order appears on the market that can fulfill your buy/sell order.
Let’s assume this is a sell order list for bitcoin (BTC):
- 0.5 BTC at $60,000 per 1 BTC
- 0.7 BTC at $61,000 per 1 BTC
- 0.1 BTC at $62,000 per 1 BTC
If you want to buy 0.6 BTC using a market order, then the exchange will automatically match your order with the first selling order for 0.5 BTC and would purchase the remaining 0.1 BTC by partially fulfilling the second order. That would cost you a total of $36,100 (0.5*$60,000 + 0.1*61,000).
This is only an example to help you understand how orders work on centralized crypto exchanges. Usually, an exchange has many orders for the listed cryptocurrencies.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs)

A decentralized exchange (DEX) allows trades to happen directly between peers. Unlike centralized exchanges, there is no central entity to oversee trades on a DEX.
DEXs allow traders to be truly anonymous, as they do not mandate a KYC, and the crypto funds you trade are held in the trader’s crypto wallet. These type of exchanges are at the heart of decentralized finance (DeFi) and function as a decentralized application (DApp) built on top of a smart contract blockchain.
Unlike centralized exchanges, DEXs do not support fiat trades, and traders can’t link a bank or a credit/debit card. DEXs rely on liquidity pools provided by other crypto investors in exchange for a reward called yield.
How trading works on a DEX
Traders interact directly with the smart contracts on the blockchain when using a DEX. They perform these trades anonymously from their private crypto wallet, which minimizes the risk of fraud.
There are three main types of DEXs:
- Automated Market Makers (AMM)
- Order books DEXs
- DEX aggregators
Automated market makers (AMMs)
The Automated Market Maker (AMM) model relies on smart contracts to fulfill peer-to-peer trades. Instead of using buy and sell orders, an AMM relies on blockchain oracles to get information about the crypto prices. It then uses liquidity pools to offer digital assets to the traders.
Liquidity pool providers (LPs) are locking a cryptocurrency pair in one of the liquidity pools on the DEX in exchange for a portion of the trading fees. Each DEX and each liquidity pool may have different rewards, similar to bank interests, but higher in value. Users who wish to provide liquidity need to deposit an equivalent value for each digital asset, as liquidity can only be offered in pairs. This process is called liquidity mining.
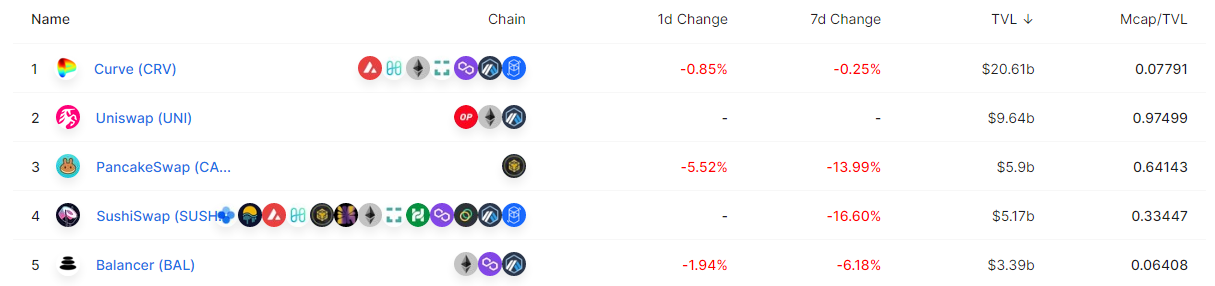
AMM decentralized exchanges are ranked by the Total Value Locked (TVL) in their smart contracts.
The main disadvantage of using an AMM exchange is the lack of liquidity, which results in high slippage fees for traders. Liquidity providers may also suffer impermanent loss while providing liquidity, but this can be offset by the rewards generated by the trading fees.
How do AMMs work?
Unlike traditional exchanges that use order books, Uniswap uses the AMM model, which utilizes liquidity pools that contain a trading pair to settle trades. During trades, the price of the assets change, so a dynamic calculation of the new rate must take place. These trades happen directly within the pool.
However, liquidity pools serve many traders, and cryptocurrencies are famous for their price volatility. That’s why slippage, a percentage difference between the quoted and executed price, occurs.
/Related
More ArticlesA high slippage percentage may be needed for trades with low liquidity, and large trades tend to have a higher slippage. Just like market orders, you can only buy at the price the market is willing to sell.
Traders can select a custom slippage tolerance for each trade. For instance, if you select a 5% slippage tolerance, it means that the received tokens after the trade could be 5% more or less than the initial amount shown.
Order book DEXs
Similar to the traditional centralized crypto exchanges, order book DEXs can have both on-chain order and off-chain order books. Usually, on-chain order books store the trade information on it, and the traders have their funds in their wallets.
These exchanges often allow traders to leverage funds borrowed from lenders from the same platform. This feature enhances the potential profit from trades, but it can also pose higher risks. Unfavorable trades can result in liquidation. Lenders earn interest on the loaned funds.
DEXs that hold the order book off-chain are somewhat similar to centralized exchanges, and this helps reduce fees and increase speed. These DEXs also suffer from liquidity crisis.
DEX aggregators
DEX aggregators use mechanisms specifically designed to solve the liquidity issues associated with it. In essence, these platforms use liquidity from multiple DEXs to optimize swaps and decrease slippage and other fees. Doing so offers the best price on the market in the shortest amount of time.
Decentralized exchange trades
Unlike centralized exchanges, traders only need a compatible crypto wallet to access a DEX.
There are several smart contract blockchains that have DEXs, and each has different transaction fees.
After deciding the network, you will need a compatible wallet for that network and the native token of that network in the wallet to start trading. The native token is used to pay the network fees.
To trade on a DEX, you need to:
- Decide what network you want to use (Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, BSC, etc.)
- Have a compatible wallet for that network
- Visit the DEX and connect your wallet.
- Start trading
What is Uniswap?

Uniswap is the largest decentralized exchange protocol on the Ethereum network. The Uniswap protocol is open-source, and it uses the automated liquidity protocol.
The Uniswap DEX allows anyone to list their token for free. New users quickly understand how to use Uniswap and can start to swap tokens without registration.
Uniswap was launched in November 2018 by Hayden Adams, a former engineer at Siemens.
In May 2020, Uniswap V2 was launched, which enabled the exchange to eliminate the requirement to deposit digital asset pairs to liquidity pools. The DEX allows direct swaps between ERC20 tokens, while reducing the number of transactions and gas prices.
In September 2020, Uniswap launched its governance token, UNI.
Launched in May 2021 on Ethereum layer 1 and on Optimism layer 2, Uniswap V3 added concentrated liquidity and multi-fee tiers features.
As with all DEXs, traders control their funds and do not have to deposit it on the exchange. Traders using Uniswap are not at risk of losing their funds as they have full custody of their assets.
The exchange supports all Ethereum compatible wallets, such as MetaMask. As of November 2021, Uniswap has a total value locked of over $10 billion, according to DappRadar.
Liquidity pools on Uniswap
Traders interact with a liquidity pool when trading on an AMM exchange such as Uniswap. When a trader executes a trade, the smart contract sends his/her funds to the liquidity pool. It then calculates the corresponding amount of the other asset and sends it back to the trader.
The trade is calculated using the formula X*Y=K, where X and Y are the amounts of each asset and K is a predefined constant.
Each trade has a slippage, which increases with large trades. At the same time, users can become liquidity providers.
Uniswap (UNI) token
In September 2020, Uniswap launched UNI, the protocol’s governance token. Uniswap’s native token enables holders to vote for changes and platform developments, including fee structure changes and distribution of tokens.
It is rumored that the UNI token was launched to counteract the SushiSwap development.
SushiSwap is a fork of Uniswap that was incentivizing users to relocate their funds to their platform with SUSHI tokens. One month later, the UNI token was launched.
At genesis, the total supply of 1 billion UNI was minted, and 15% were distributed between past and present users. All Uniswap traders received 400 UNI. Another 40% was distributed between the team and investors.
UNI token could be a profitable long-term investment, as Uniswap V3 announced cheaper gas prices, and the Optimism deployment will offer significantly lower fees.
Uniswap UNI token is available on most the exchanges, such as Binance, Coinbase, Huobi, and Gate.io.
How do cryptocurrency swaps work?
It’s needless to say that it’s less time-consuming and cost-efficient to perform crypto-to-crypto exchanges than converting a cryptocurrency to fiat before buying another cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency swap services such as Uniswap may come in handy when trying to perform a trade between two cryptocurrencies with low liquidity. Swapping crypto is easy, fast, affordable, and secure.
If, for instance, you would like to trade ENJ for CHR, you would have to first exchange ENJ for a more established coin such as ETH or DAI and then buy CHR using ETH or DAI. This is a long and not so effective process. You would also have to consider the volatility of the prices, resulting in a loss while performing these individual trades.
To counteract this deficiency, trading platforms implemented the instant swap feature, allowing traders to change one crypto for the other instantly.
The swap platform takes care of the conversions, and traders pay the transaction fee only once.
How to use Uniswap Exchange
You will need to have a compatible wallet before learning how to use the Uniswap exchange. Since the DEX is an Ethereum-based, you can use a wallet that supports the Ethereum network.
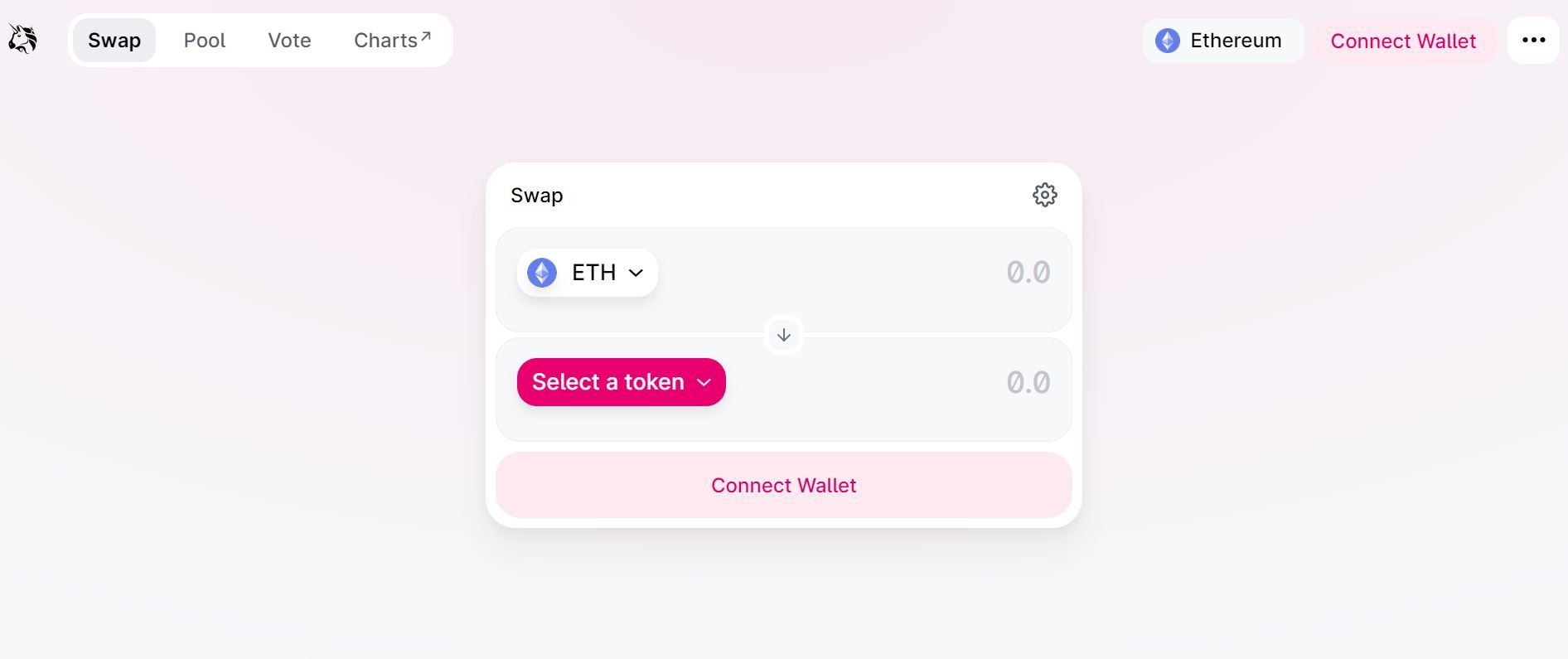
Step 1. Connect your wallet
Go to Uniswap and click Connect Wallet, in the top-right corner.
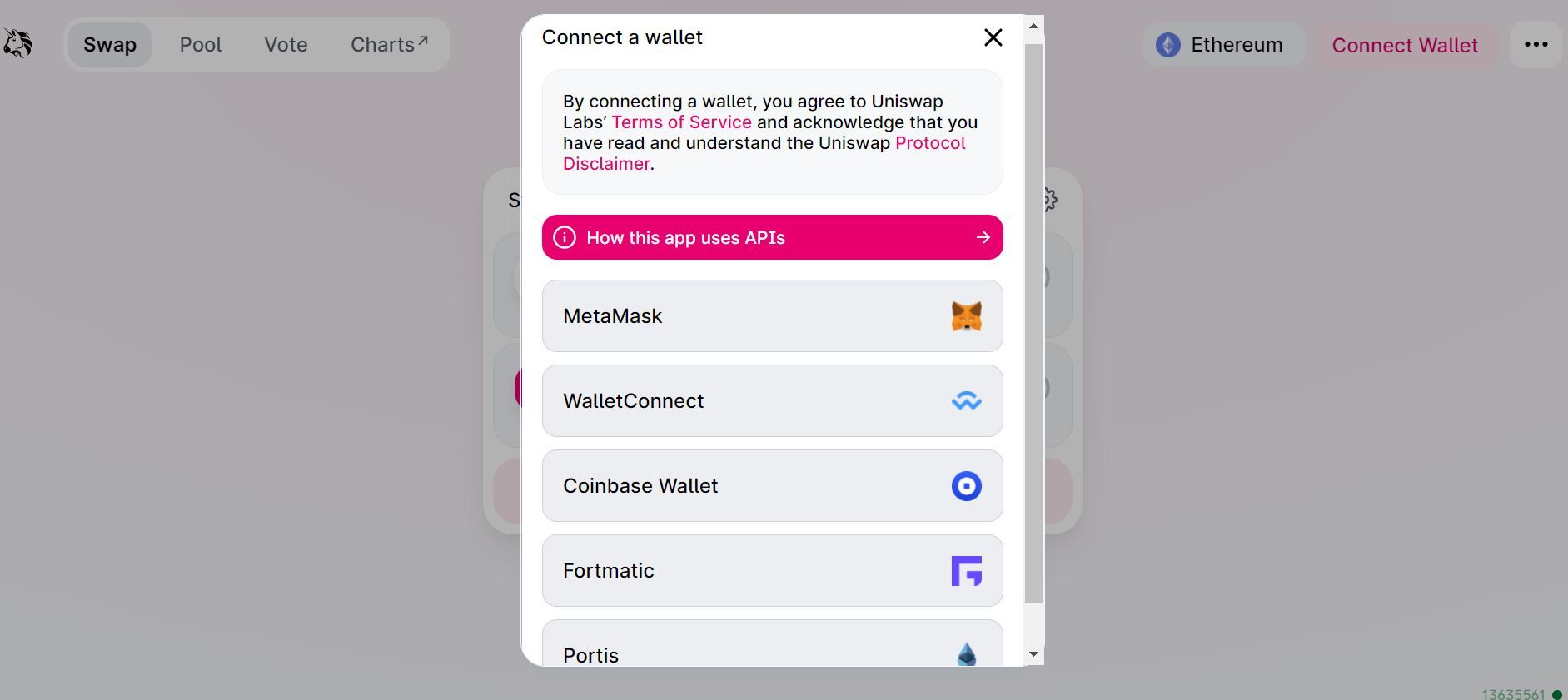
Step 2. Select a wallet
You will be given a list of supported wallets. MetaMask is one of the most popular options for Ethereum.
Note that WalletConnect supports many wallets, and can be used by scanning the QR code if you are using the mobile app.
Step 3. Confirm connection
You will be asked to confirm the connection, either in your browser or on the mobile app.
How to swap crypto on Uniswap Exchange
After you have connected your wallet to Uniswap, you can start swapping tokens on the platform.
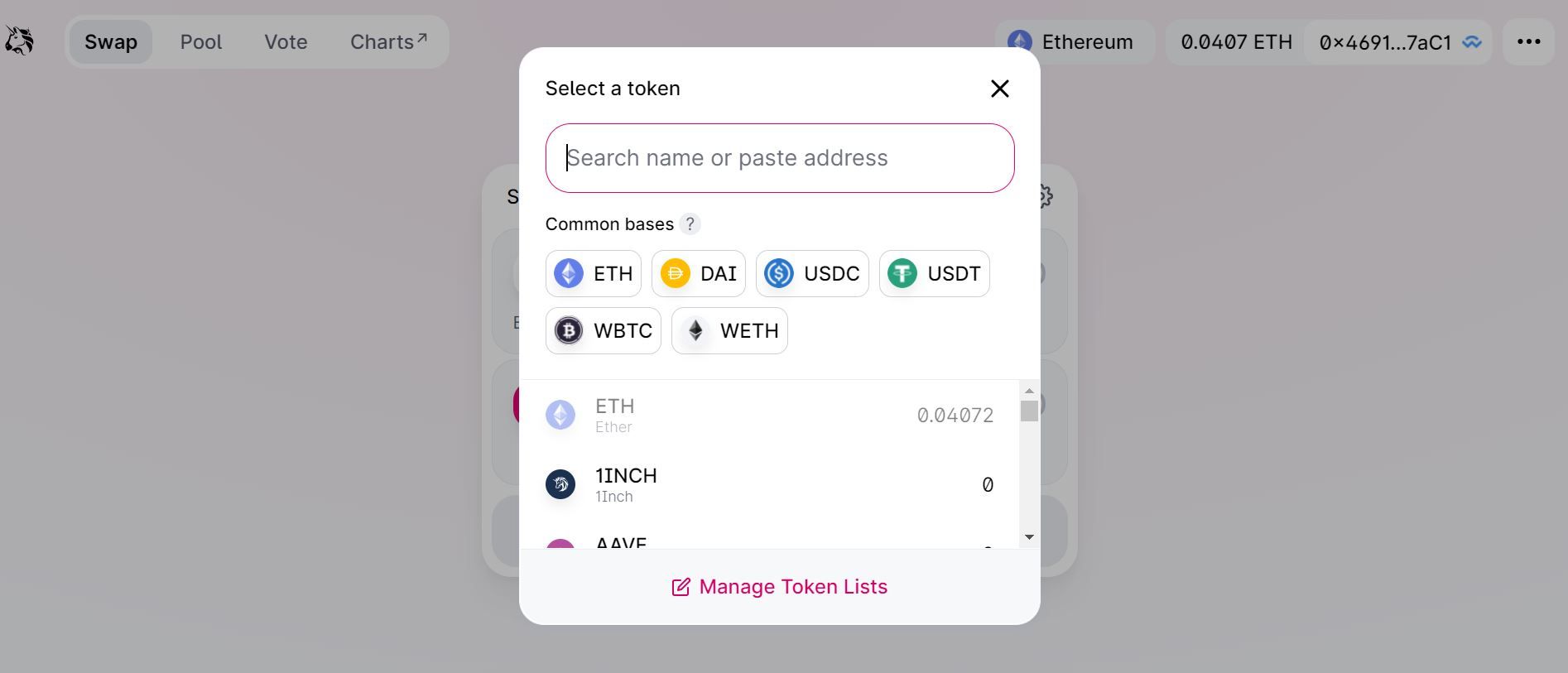
Step 1. Select the crypto you want to swap
First, you need to select the crypto you want to swap. You can search tokens by name or address.
Step 2. Enter the amount of crypto you want to swap
Assuming you have funds for the crypto you want to use for the swap, you have to enter the amount of crypto you want to swap. Uniswap will automatically calculate the amount of the other token that you will receive.
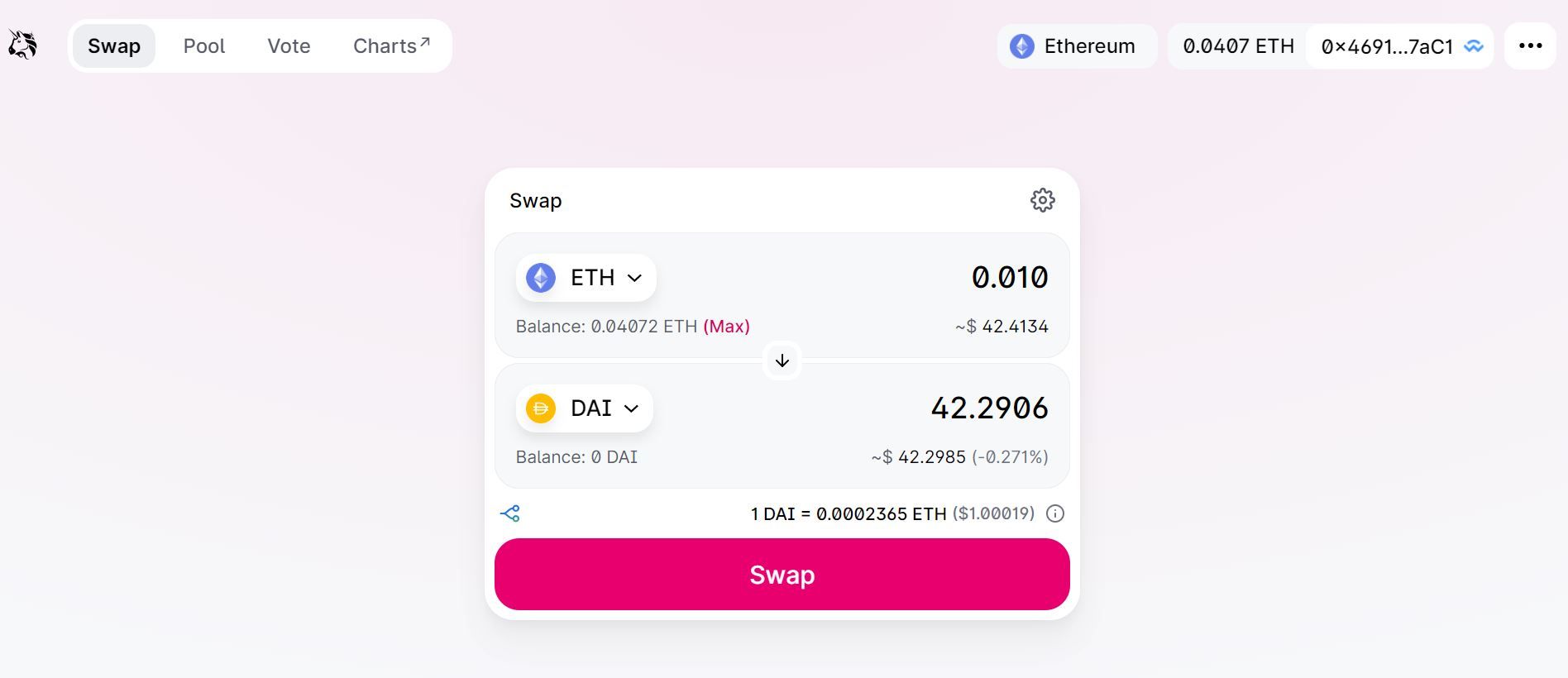
Let’s assume you want to swap ETH for DAI. If you want to exchange a specific amount of ETH, then you would have to enter that amount in the ETH field. If you desire a specific amount of DAI, you can enter that amount in the field of DAI amount.
Step 3. Review and confirm the swap
If you agree with the rate and amount that you will receive, click on Swap, and you will see a new window where you can review the details of your swap.
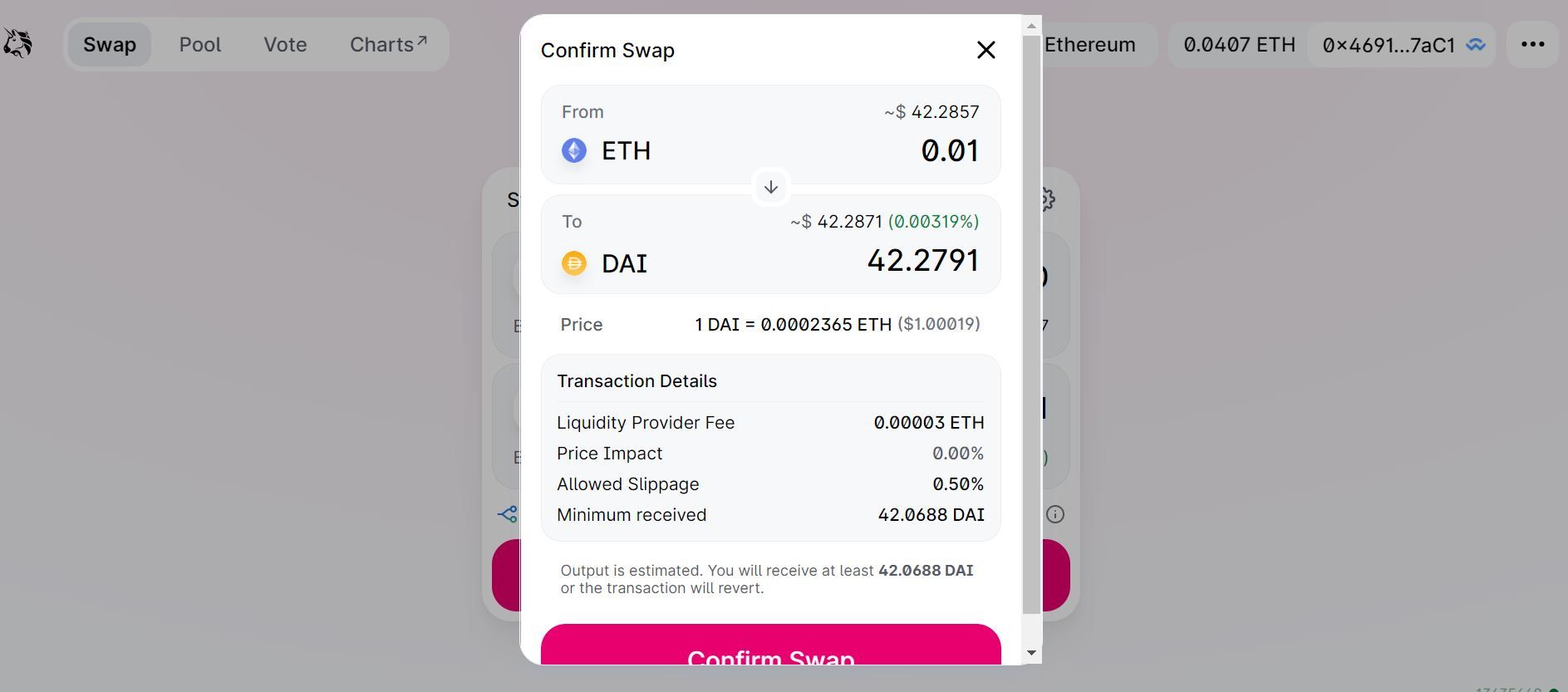
Click Confirm Swap to continue and execute the swap.
You will see the funds in your wallet as soon as the swap has been confirmed.
How to add liquidity on Uniswap
If you already have some cryptocurrency that you want to hold but also want to generate a passive income using those funds, you can provide submit your funds to a liquidity pool on Uniswap. Note that you will need to provide a pair of two tokens.
So, how to use Uniswap to earn a passive income? Become a liquidity provider (LP).
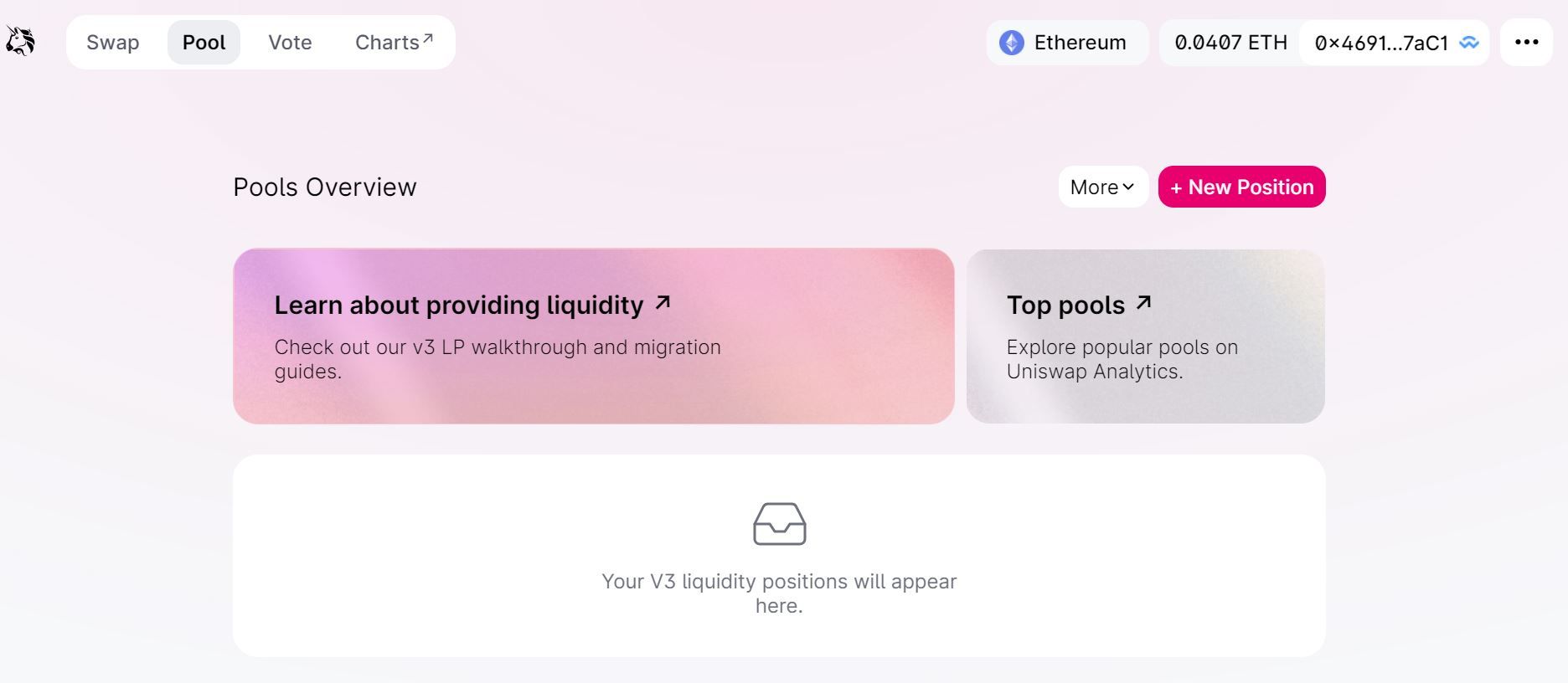
Step 1. Select tokens for liquidity mining
Go to Pool and then click + New Position to select the trading pair that you wish to submit as liquidity.
Note that you can even add a new token.
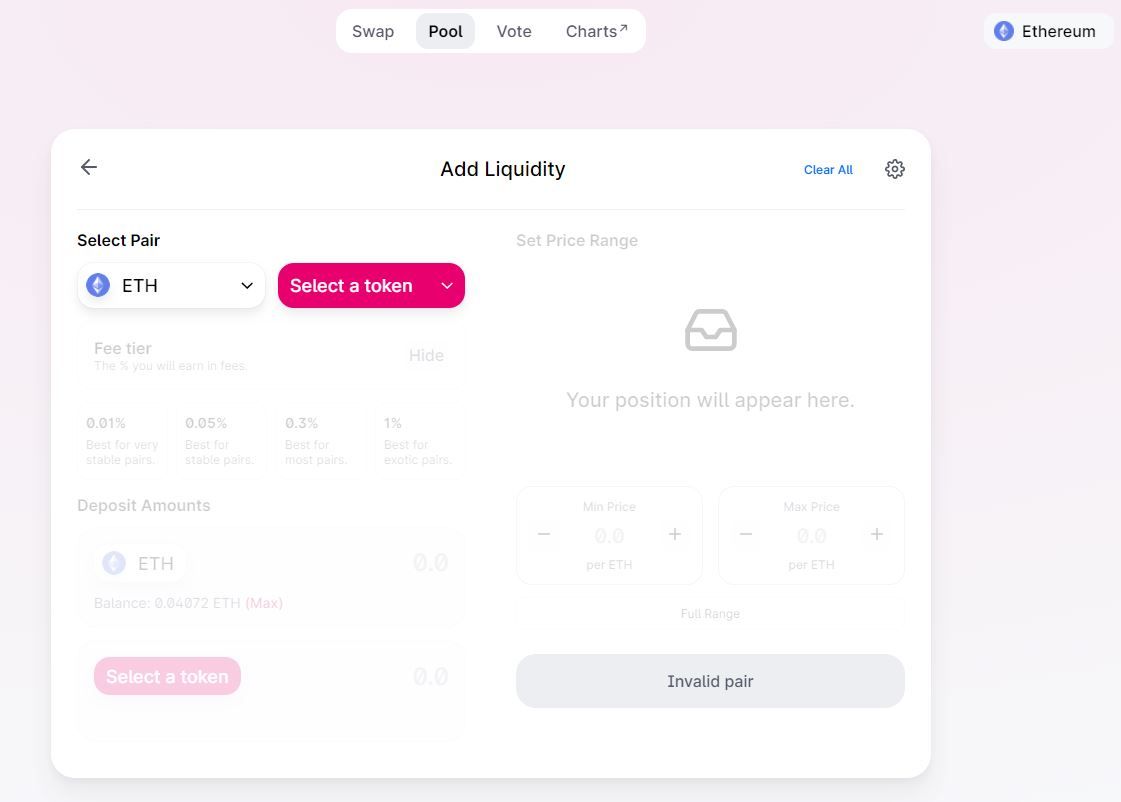
Step 2. Select amount for liquidity mining
Next you need to select the amount you want to provide to that liquidity pool. Note that you need to provide the corresponding ratio for each trading pair.
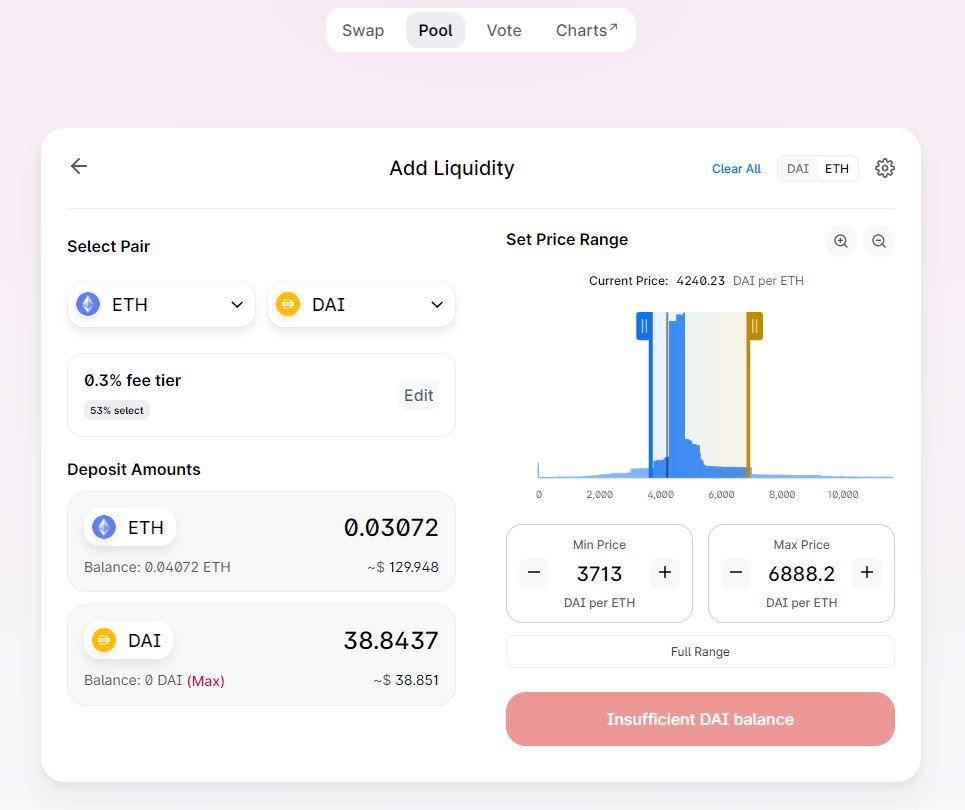
Step 3. Review and confirm Supply
After entering the desired amount for both assets, you will have to approve the Ethereum transaction and pay the gas fees. Afterwards, click Supply and you will receive the LP tokens in your wallet, and you will see the liquidity pool share. The pool share is a ratio to tell you how much of that pool you own.
Uniswap vs. SushiSwap

Uniswap and SushiSwap are two DEXs built on the Ethereum blockchain,
While Uniswap is the leading DEX regarding exchange volume, SushiSwap offers features such as yield farming and special bonuses for SUSHI token holders.
SushiSwap is a fork of Uniswap, an open-source platform that offers the same core products. Both these DEXs are AMMs on the Ethereum network. Users can provide liquidity on both platforms and earn a passive income.
However, there are a few differences between Uniswap and SushiSwap.
Uniswap V3 allows concentrated liquidity positions, i.e., NFTs stored in your Ethereum wallet, just like any other token. This is a novelty in the DeFi world.
Uniswap also offers multiple fee tiers, and they are paid to the liquidity pool. On SushiSwap, the 0.3% trading fee is divided between the liquidity pool (0.25%) and SUSHI token holders (0.05%). If you want to hold SUSHI, you will earn more on SushiSwap, but liquidity providers will earn more on Uniswap.
Besides the swap functionality, SushiSwap also incorporated a yield farming platform, which allows compounding your yield. Some pools have impressive annual percentage yield (APY), but investors should be aware that this is a risky investment strategy. SushiSwap allows wrapped tokens for yield farming.
Should you use Uniswap?
Now that you know how to use Uniswap, you should think about whether you should use it. The truth is, Uniswap is one of the most reliable and popular DEXs available. It supports several features and because it’s a DEX, has multiple advantages over a centralized exchange.
If you’re looking to get into DeFi, then Uniswap is a great place to start. You could, of course, consider other DEXs, but there’s no reason for a beginner interested in DeFi not to at least try Uniswap.
< Previous In Series | Exchanges | Next In Series >
Frequently asked questions
How do I use Uniswap?
What is Uniswap and does it work?
How do you buy coins on Uniswap?
Can U.S. citizens use Uniswap?
How much is UNI worth?
Trusted
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.








